Difference between revisions of "Contiki Coffee File System"
From Contiki
(→cfs_open) |
(→Data Structure Used In The System) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<source lang="c"> | <source lang="c"> | ||
struct file_desc { | struct file_desc { | ||
| − | cfs_offset_t offset; | + | cfs_offset_t offset; |
| − | struct file *file; | + | struct file *file; // a file pointer which point to the corresponding file. |
| − | uint8_t flags; | + | uint8_t flags; //flag used to indicate the open mode of the file and whether the fd is free. |
#if COFFEE_IO_SEMANTICS | #if COFFEE_IO_SEMANTICS | ||
uint8_t io_flags; | uint8_t io_flags; | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[File:Datastr.png]] | [[File:Datastr.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <source lang="c"> | ||
| + | static int | ||
| + | get_available_fd(void) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int i; | ||
| + | |||
| + | for(i = 0; i < COFFEE_FD_SET_SIZE; i++) { | ||
| + | if(coffee_fd_set[i].flags == COFFEE_FD_FREE) { | ||
| + | return i; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return -1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contiki is a Linux like system, everything is a file, and the opened file is represented by the file descriptor. The get_available_fd will return the smallest available fd by check the file_desc array in an ascending order, the first one with flag == 0(COFFEE_FD_FREE) is what we want. If all the flags are set, then return -1. | ||
=== cfs_open === | === cfs_open === | ||
Revision as of 18:36, 8 November 2014
Contents
Introduction
This tutorial is a introduction to cfs_open function of Coffee file system on Contiki OS 2.7.
You Will Learn
Through this tutorial you will learn about how the Coffee file system works.
Source Code
~/contiki-2.7/core/cfs/cfs-coffee.h
~/contiki-2.7/core/cfs/cfs-coffee.c
Coffee File System Open File
Data Structure Used In The System
struct file_desc {
cfs_offset_t offset;
struct file *file; // a file pointer which point to the corresponding file.
uint8_t flags; //flag used to indicate the open mode of the file and whether the fd is free.
#if COFFEE_IO_SEMANTICS
uint8_t io_flags;
#endif
};struct file_desc coffee_fd_set[COFFEE_FD_SET_SIZE];static int
get_available_fd(void)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < COFFEE_FD_SET_SIZE; i++) {
if(coffee_fd_set[i].flags == COFFEE_FD_FREE) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}Contiki is a Linux like system, everything is a file, and the opened file is represented by the file descriptor. The get_available_fd will return the smallest available fd by check the file_desc array in an ascending order, the first one with flag == 0(COFFEE_FD_FREE) is what we want. If all the flags are set, then return -1.
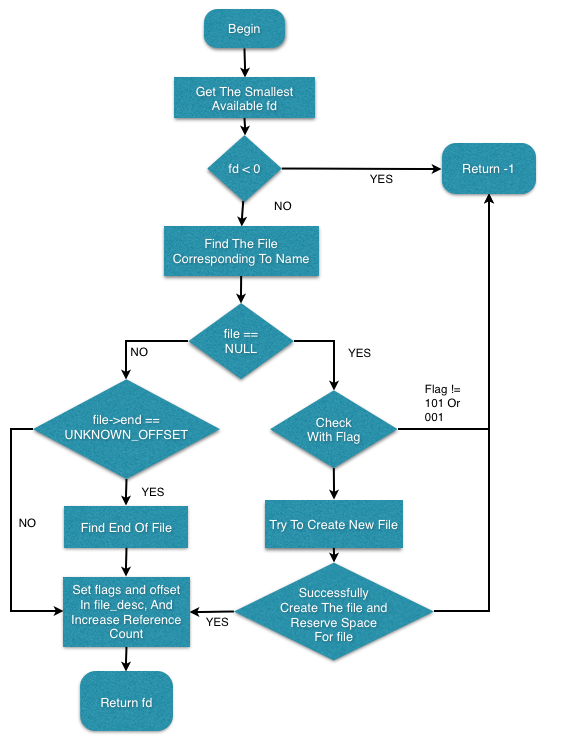
cfs_open
cf_open is used to open a file. If it successfully open the file then it returns the file descriptor(fd), otherwise it returns -1.
cfs_open source code:
int
cfs_open(const char *name, int flags)
{
int fd;
struct file_desc *fdp;
fd = get_available_fd(); //find the smallest available fd, see section 4.1
if(fd < 0) {
PRINTF("Coffee: Failed to allocate a new file descriptor!\n");
return -1;
}
fdp = &coffee_fd_set[fd];
fdp->flags = 0; //set the fd to FREE
fdp->file = find_file(name); //find the file corresponding to name(not exist, In flash but not buffered, buffered)
/*** if there isn't any corresponding file, then try to create new file ***/
if(fdp->file == NULL) {
if((flags & (CFS_READ | CFS_WRITE)) == CFS_READ) {
return -1;
}
fdp->file = reserve(name, page_count(COFFEE_DYN_SIZE), 1, 0);
if(fdp->file == NULL) {
return -1;
}
fdp->file->end = 0; // Since it's a new created file, the end will be set to 0
}
/*** find the file,seek for the end of the file***/
else if(fdp->file->end == UNKNOWN_OFFSET) {
fdp->file->end = file_end(fdp->file->page);
}
fdp->flags |= flags;
fdp->offset = flags & CFS_APPEND ? fdp->file->end : 0; //if the flag is set to APPEND, then the offset is set to the end of the file, otherwise set to 0
fdp->file->references++; //reference count will increment
return fd;
}